VM Placement During Provisioning
One of the stages in the VMProvision_VM State Machine is Placement, and it's here that the decision is made where to create the new VM, i.e. which Cluster, Host and Datastore.
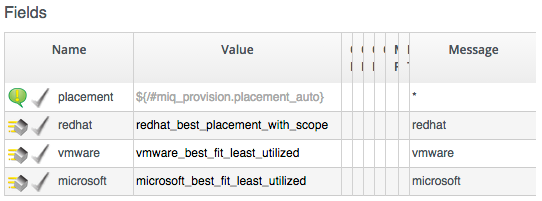
The value for the Placement stage in the template Instance of this State Machine is:
/Infrastructure/VM/Provisioning/Placement/default#${/#miq_provision.source.vendor}
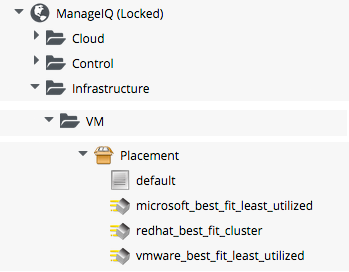
The default Instance is as follows:
We see that the Provider-appropriate best-fit method is selected by a message. The redhat_best_fit_cluster Method just places the new VM into the same cluster as the source template. The other two Methods select the Host with the least running VMs, and most available Datastore space.
Customising Placement
As part of the added-value that CloudForms brings over ManageIQ, the RedHat Domain includes improved placement Methods that we can optionally use:
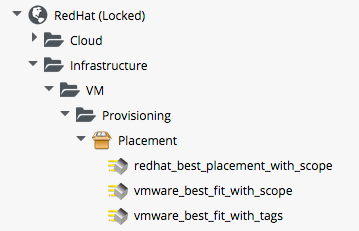
The *_with_scope Methods allow us to apply a tag from the prov_scope (Provisioning Scope) tag category to selected Hosts and Datastores. This tag indicates whether or not they should be included for consideration for automatic VM placement. The prov_scope tag should be "all", or the name of an Access Control User Group. By tagging with a group name, we can direct selected workloads (such as developer VMs) to specific Hosts and Datastores.
The vmware_best_fit_with_tags Method considers any Host or Datastore tagged with the same tag as the provisioning request, i.e. selected from the Purpose tab of the Provisioning Dialog.
All three RedHat Domain Methods also allow us to set thresholds for Datastore usage in terms of utilisation percentage, and number of exiting VMs, when considering Datastores for placement.
Using Alternative Placement Methods
To use the RedHat Domain placement Methods (or any others that we choose to write), we copy the ManageIQ/Infrastructure/VM/Provisioning/Placement/default Instance into our own Domain, and edit the value for the redhat, vmware, or microsoft schema fields as appropriate to specify the name of our preferred Method.